Article of the
Month - May 2022
|
EU Space Programmes for Geomatics
Maria RUIZ MOLINA, Teresa MARTINEZ RECHE, Ana SENADO GARCÍA, Eduard
ESCALONA, Spain
 |
 |
 |
 |
Eduard Escalona
(EUSPA) |
Ana Senado
(Galileo) |
Maria Ruiz
(EGNOS) |
Teresa Martinez
(Copernicus) |
This article in .pdf-format (27 pages)
This
article provides an overview about the EU Space Programmes
Galileo, EGNOS and Copernicus, their synergies and applications for
geomatics' users. This article will be presented at the FIG Congress
2022 in Warsaw, Poland.
SUMMARY
The evolution of the European GNSS Agency (GSA) into the European
Union Agency for the Space Programme (EUSPA)
sets the start of a new era for EU Space. EUSPA will create even more
opportunities for EU citizens and the economy, in particular by
leveraging synergies between the space programme components on the
downstream market, especially for GNSS and Earth observation, playing a
key role in the development of downstream applications.
This article provides an overview about the EU Space Programmes Galileo,
EGNOS and Copernicus, their synergies and applications for geomatics’
users.
2. Galileo
2.1 What is Galileo
Galileo is the European Global Navigation Satellite System (EGNSS)
that provides satellite positioning services worldwide. The Galileo
system was designed focusing on the civil citizens, making it
independent from military entities and allowing the provision of a full
range of services that ease the development of multiple applications at
user level.
Galileo is currently providing three different services: Galileo Open
Service (OS) and Galileo Search and Rescue (SAR), which are accessible
to civil users, and the Galileo Public Regulated Service (PRS) which is
delivered to governmental and authorized users.
2.2 Galileo Services
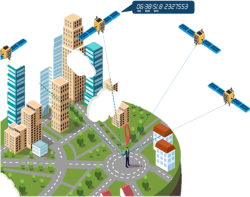
Galileo Open Service (OS)
Galileo OS is a free of charge positioning and timing service
available worldwide. Galileo OS offers the Galileo OS Ranging Service,
allowing users to estimate their distance to the satellite, the Galileo
OS UTC Time Determination Service, providing with a direct and accurate
access to Universal Time Coordinated (UTC) and the Galileo OS
Positioning Service which allows Galileo receivers to estimate their
position through combination of ranging and timing measurements.
| Galileo provides ranging signals in three
different frequency bands, enabling single- and dual- frequency
positioning for users equipped with suitable receivers.
The receivers may be single frequency (SF) or
double frequency (DF). SF receivers extract navigation
information from any of the three frequencies (E1, E5a and E5b)
while a DF receiver extracts information from a combination of
E1 and E5a or E1 and E5b. A DF solution allows compensation of
the ionospheric errors, thus provides better performance to the
user. How the receiver understands the Galileo OS signals is
explained in the
Galileo OS Signal In Space Interface Control
Document (OS SIS ICD). |
 |
|
Figure 1: Galileo OS positioning and timing service
|
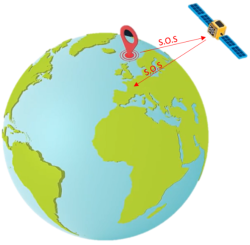
Galileo Search and Rescue (SAR)
|
Galileo offers a significant contribution to the Search and
Rescue service (SAR), an international life-saving service
managed by
COSPAS-SARSAT. Contribution from Galileo to SAR service is
twofold. In the first place, Galileo satellites re-transmit
distress alert signals from SAR beacons to the corresponding
rescue centers in ground. This is crucial for a fast detection
of distress beacons.
On the second place, with the Galileo Return link service,
Galileo will also provide a return signal, letting people know
that their signal has been received. This acknowledge message
reduces the stress of people while they wait for the rescue
team.
|
 |
| |
Figure 2: Galileo contribution to COSPAS-SARSAT
|
2.3 Future Galileo Services
Once fully deployed, Galileo will offer two new services: Galileo
Open Service Navigation Message Authentication (OSNMA), which will allow
users to authenticate Galileo navigation messages and Galileo High
Accuracy Service (HAS), which will offer orbit and clock corrections to
be processed by users‘ receivers and obtain decimeter accuracies.
- Galileo OSNMA provides receivers with the assurance that
the received Galileo navigation message is coming from the system
itself and has not been modified. OSNMA is authenticating data for
geolocation information from the Open Service through the Navigation
Message (I/NAV) broadcast on the E1-B signal component. This is
realized by transmitting authentication-specific data in previously
reserved fields of the E1 I/NAV message. By using these previously
reserved fields, OSNMA does not introduce any overlay to the system,
thus the OS navigation performance remains untouched. Besides, those
receivers already tracking OS signals will only need a firmware
update to start authenticating the navigation data. Additional
details about OSNMA service can be found in
Galileo Open Service Navigation Message Authentication (OSNMA) Info
Note.
- Galileo HAS provides free of charge high accuracy Precise Point
Positioning (PPP) corrections through the Galileo signal (E6-B) and
by terrestrial means (Internet). The corrections are composed by
orbits, clocks, code and phase biases per each satellite. The HAS
full service will include atmospheric corrections too. Additional
details about HAS service description can be found in Galileo
High Accuracy Service (HAS) Info Note.
2.4 Galileo in Geomatics
Geomatics professionals are already benefitting from using EGNSS in a
multi-constellation and multi-frequency environment, providing higher
availability, continuity and better results in harsh conditions. This is
the result of new developments in receiver technologies, evolution in
terms of price and usability and proliferation of augmentation services
which are diverse, accurate and profitable.
The stringent accuracy demands across the various surveying
applications such as land surveying (cadastral, construction and mine),
mapping and marine surveying (marine cadastre, hydrographic and offshore
surveys) benefit from the proliferation of high accuracy GNSS-based
solutions. This is due to the number of differential correction
networks/services and the increased affordability of high-accuracy
receivers. The future Galileo HAS- which will target decimetre-level
accuracy-will be a good candidate to cover accuracy demand on
applications such as GIS and mapping.
2.5 Success stories
Below there is an example of projects where EGNSS, and in particular
Galileo, is a key enabler to develop innovative applications:
3. EGNOS
3.1 What is EGNOS
EGNOS (European Geostationary Navigation Overlay Service) is the
European regional satellite-based augmentation system (SBAS) which
provides corrections and integrity information to GPS signals. Although
it was initially designed for aviation, it has proved to be useful in
other markets such as geomatics, maritime and agriculture.
EGNOS provides three services offering different performances adapted
to satisfy each user´s requirements. Geomatics activities can benefit
from both the EGNOS Open Service (OS) and EGNOS Data Access Service
(EDAS) while the EGNOS Safety of Life Service provides integrity and it
is tailored to safety-critical transport applications.
3.2 EGNOS Services
The EGNOS Open Service is accessible free-of-charge in Europe to any
user equipped with an appropriate GPS/SBAS compatible receiver for which
no specific receiver certification is required. Neither a base station
nor internet connection is needed, just access to the EGNOS Signal in
Space.
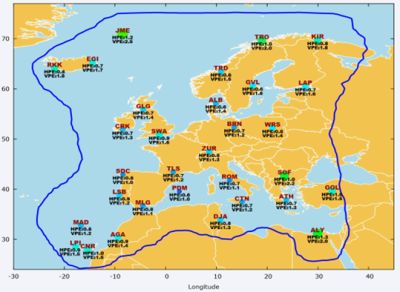
The next picture shows an example of the values of the EGNOS Open
Service accuracy in Europe, measured at Ranging Integrity Monitoring
Stations (RIMS) during 6 months. HPE refers to the Horizontal Position
Error and, as it can be seen, it is common to reach sub-metric
accuracies (expressed as 95% percentile) when using EGNOS.
Source:
EGNOS Open Service (OS) Service Definition Document
- The other EGNOS Service which may be used by geomatics
applications is the EGNOS Data Access Service (EDAS), addressed to
users that require enhanced performance for commercial and
professional use. It offers access to EGNOS data through the
Internet improving accuracy, reliability and availability of GNSS
information.
In particular, EDAS provides ground-based access to EGNOS data
through a collection of services. The most common services in geomatics
are:
- EDAS SISNeT: Access to messages from EGNOS GEO satellites
transmitted through the Internet using the SISNeT protocol. A device
with internet connection is required, including a software tool
implementing SISNeT protocol.
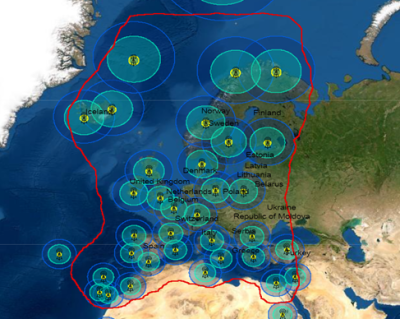
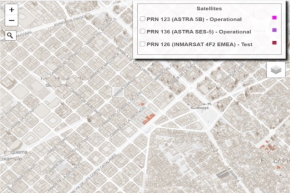
- EDAS-based NTRIP: DGNSS and RTK corrections provided through
Internet in the surroundings of the EGNOS RIMS. A DGNSS and/or RTK
receiver compatible with the NTRIP protocol is required. The
available positioning solutions based on EDAS in the area can be
seen in the EDAS RTK and DGNSS coverage map:
Source:
EDAS DGNSS Coverage Map
3.3 EGNOS Visibility Maps
EGNOS is available over all Europe, but the terrain orography and
artificial obstacles such as high buildings could affect the visibility
of EGNOS geostationary satellites broadcasting the GPS corrections. In
order to support the users to identify EGNOS “shadow areas”, the EGNOS
Visibility Maps allow visualizing natural and urban areas where there is
no visibility of one or both EGNOS operational geostationary satellites.
Source:
EGNOS Visibility Maps (left on country side, right on urban
environment)
3.4 EGNOS in Geomatics
GNSS is a key enabler for geomatics applications which involve the
geo-data collection means and techniques used in land surveying
(including cadastral, construction, mining or infrastructure
monitoring), photogrammetry, remote sensing, marine surveying and other
emerging applications, such as those based on drones or mobile mapping.
EGNOS in particular may support geospatial data acquisition in those
scenarios in open space, with sub metric accuracy requirements and
without internet access. That is the case of the following applications
in geomatics:
- Management of natural areas: Forests and parks, camping areas,
wind farms.
- Management of utility networks: Water, electricity,
telecommunications.
- Inventory and control of assets in open areas: Urban furniture,
traffic signs.
- Taking of samples in field campaigns: Environmental law
enforcement agents, biologists, archaeologists.
- Determination of perimeters and areas: Municipality borders,
urban planning, green cadastre, construction, dumping sites.
To sum up, the main advantages of EGNOS in geomatics are:
- EGNOS is a free-of-charge service
- EGNOS provides stable and continuous corrections in real time
- EGNOS signal is provided by satellite:
- Wide coverage over Europe
- No SIM card, no base station, no radio link, etc.
- Real time solution
- Almost all professional mapping and surveying devices are
EGNOS-enabled. Users just have to activate it in an easy and
friendly way.
3.5 Succes stories
There are many success stories which evidence the benefits of EGNOS.
Some examples are detailed
below.
4. COPERNICUS
4.1 What is Copernicus
Copernicus, previously known as Global Monitoring for Environment and
Security (GMES), is the European
Union's Earth observation programme coordinated and managed by the European
Commission in partnership with the European
Space Agency (ESA), the EU
Member States and EU
agencies.
One of the main goals of EUSPA is to foster the use of EU space
technologies. In particular, for Copernicus, EUSPA will focus on
increasing the downstream market uptake of Copernicus, leveraging the
synergies with the European Navigation Satellite Systems (EGNSS),
Galileo and EGNOS.
The main objective of Copernicus is to achieve a global, continuous,
autonomous, high quality and large amount of reliable and up to date
information on the status of our planet. Copernicus observes the
environment, collects, stores, analyses data and provides products to
enable effective decision-making. The data are analysed in a way that
generate indicators useful for researchers and end users providing
information on past, present and future trends. Therefore, Copernicus
contributes to improve the management of the environment, understand and
mitigate the effects of climate change and ensure civil security.
The vast majority of data delivered by Copernicus is made available
and accessible to any citizen, and any organisation around the world on
a free, full, and open basis, delivering 20 terabytes per day of data
and information.
4.2 Components of Copernicus
The implementation of the programme is under the responsibility of
the European Commission for its three components: Space, Services and
In-situ.
- Space Component is composed for two satellite missions:
- Sentinel constellation: the six Sentinels satellites are the
core or Space component, and are being developed for the
specific needs of the Copernicus programme
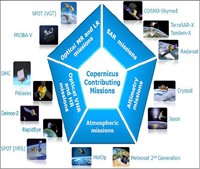
- Contribution Missions: missions from other spaces agencies
to complement Sentinel mission and other requirements
- The six Copernicus Services (Land Monitoring, Marine Environment
Monitoring, Atmosphere Monitoring, Emergency Management, Services
for Security applications and Climate Change) produce value-added
products based on the space data served by the Sentinels and the
Contributing Missions.
- In Situ Component, used mainly for calibration and validation of
Copernicus data, can be divided into:
- Observations: environmental measurements from
measuring stations, weather balloons, sensors aboard airplanes,
ships, floats, moorings, radars
- Reference data: topographic maps (natural land surface and
man-made features), hydrography, transport networks and land
cover, digital elevation models, aerial imagery, etc.
4.3 Access to data
There are different points to access Copernicus data.
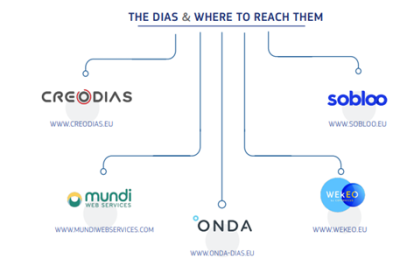
DIAS ("Data
and Information Access Services") are five new access points
available to users. All DIAS platforms provide access to Copernicus
Sentinel data, as well as to the information products from the six
operational services of Copernicus, together with cloud-based tools
(open source and/or on a pay-per-use basis)
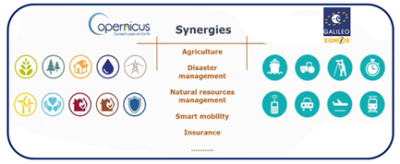
4.4 Applications of Copernicus: synergies with EGNSS
The wide availability of EO data has led to increased opportunities
in different markets. The opportunities could be divided in different
Copernicus sectors and can be explored in the
Copernicus_market_report_2019 .
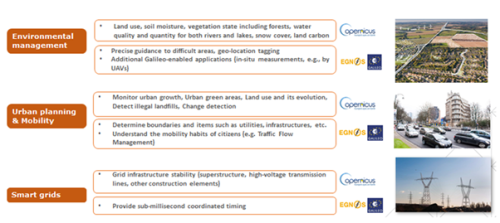
The main Copernicus applications in mapping and surveying activities
are:
- Environmental management (tree inventories…)
- Urban (urban heat islands, heritage, air quality monitoring,
thermal auditing, …)
- Smart grids
- Surveying (land, marine, hydrographic..)
- Construction and infrastructures
- Exploration and seismic surveying
- etc
Although there are applications that uses Copernicus or EGNSS
individually, there are already a number of applications that already
use both, integrated as a whole, adding value to users.
On the one hand, Copernicus often needs its data georeferenced by
GNSS, and on the other hand, typical GNSS applications can be
complemented with imagery and maps to provide context information.
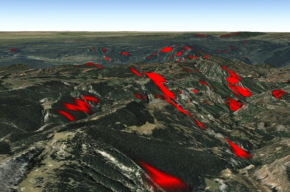
In particular, below it is presented some graphic examples that show
how Copernicus and EGNSS contribute to mapping and surveying
applications:
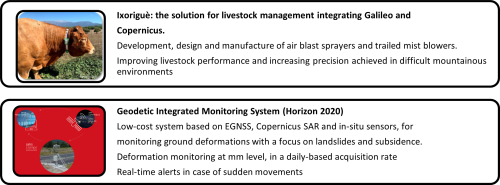
4.5 Success stories of Copernicus and EGNSS
There are already some examples that show the benefits of the
combined use of Copernicus and EGNSS. They are detailed below:
- Success stories that uses Galileo and Copernicus
Source:
European GNSS Service
Centre
- Success stories that uses ENOS and Copernicus
Source:
EGNOS User Support Website
5. Conclusions
- European Space Programmes (Galileo, EGNOS and
Copernicus) provide FREE and valuable information to any users that
can be optimally used in applications that benefit decision making
processes, contributing to sustainable development.
- EGNSS contribution is widely recognized in
mapping and surveying context providing accuracy and
georeferenced data. Fields of applications are cadastral
and constructions, infrastructure monitoring, mine surveying,
mapping & GIS, environmental management, urban planning, etc.
- EUSPA is the user-oriented operational agency
of the EU Space program, contributing to sustainable growth,
security and safety of the European Union. Therefore, one of the
main roles will be to provide more opportunities for entrepreneurs
to develop their activities based on synergies between
Copernicus and EGNSS (Galileo and EGNOS).
- The European Space Programmes, EGNSS and Copernicus, are
complementary and provide added value for
users. The combined use enhances the ability to use satellite
technologies and contributes to the benefits obtained. In fact, GNSS
is the most efficient and widespread technology for geo-referencing
and precisely time-stamping all EO measurements.
- The knowledge, awareness and contribution of
different actors is essential for a good development of
applications, including municipal authorities, policy makers,
farmers, surveyors, universities and R&D centres, private/public
companies, etc.
6. REFERENCES
https://www.euspa.europa.eu/
https://www.gsc-europa.eu/
https://egnos-user-support.essp-sas.eu/new_egnos_ops/
https://www.euspa.europa.eu/european-space/copernicus/what-copernicus
https://www.copernicus.eu/en
7. BIOGRAPHICAL NOTES and CONTACTS
Eduard Escalona Zorita, from EU Agency for
the Space Programme (EUSPA), PhD, is Space Downstream Market
Officer at EUSPA since 2019 contributing to the downstream market
development of Galileo, EGNOS and Copernicus. Dr. Escalona obtained his
MSc and PhD degrees in telecommunications engineering from the
Polytechnical University of Catalonia (UPC). He is co‐author of over 70
scientific articles in topics related to Future Internet architectures
and services.
Ana Senado García, from Galileo Service Centre, is
Telecommunications Engineer from the University of Alcalá (Spain) with
about 8 years of experience in the positioning technology sector (GNSS),
in particular, EGNOS and Galileo. Currently, her main activities are
related to Galileo service provision, Galileo system evolutions and
improvement of Galileo services to users. She has worked in transport
sector, specifically aviation and maritime. She is currently working on
the promotion and adoption of Galileo services (Open Service and Search
and Rescue Service) as well as preparing for the provision of future
services (Galileo High Accuracy Service and Open Service Navigation
Message Authentication service).
Maria Ruiz Molina, from EGNOS Service Provider holds
a Master´s degree in Telecommunications Engineering by the Technical
University of Madrid (Spain). She has been working for more than ten
years in R&D European programmes, initially in the aviation sector,
contributing to SESAR programme and afterwards in GNSS. Since 2017 she
has been working at the EGNOS Service Provider in aviation domain and
currently in agriculture and geomatics.
Teresa Martinez Reche, from EGNOS Service Provider
is Degree in Physics by University of Granada (Spain) with postgraduates
studies in Earth Observation (EO). Teresa has worked as Technical
Manager in Remote Sensing and Cartography projects. Currently she is
working for the EGNOS Service Provider, in the frame of the EGNOS
Service Adoption contract for the European Agency for the Space
Programme (EUSPA), focused in Agriculture and Geomatics market segments.
The main activities are to promote the adoption of EGNOS and assist its
users in the use of EGNOS, as well as to promote synergies between EGNOS
and Copernicus among potential interested users
Contacts
https://egnos-user-support.essp-sas.eu/
https://www.gsc-europa.eu/